Taking the analysis to the data, not the data to the analyst
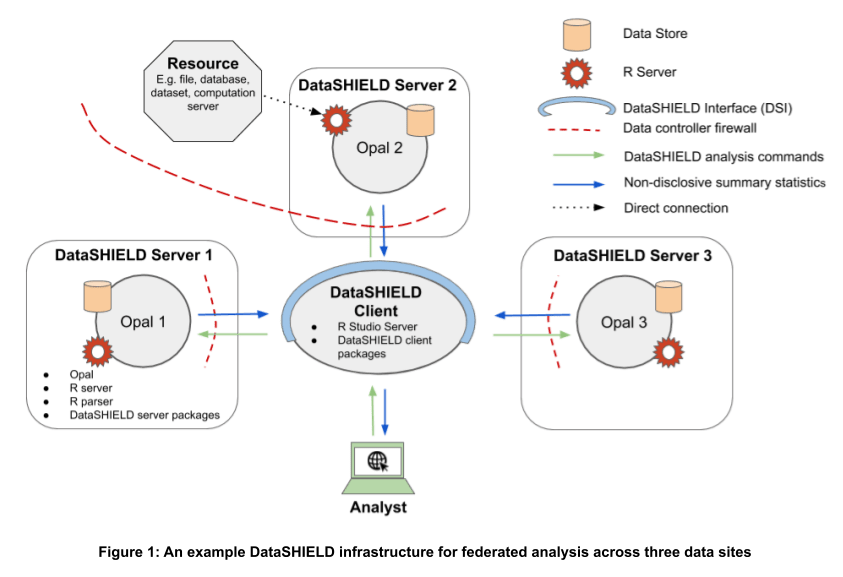
DataSHIELD is a scientifically mature, open-source data analysis platform for federated analysis with real-time disclosure control. It comprises a client-server architecture. The individual patient data remain server-side, with the data custodian and are not viewed by the analyst nor shared or moved. The role of the client-side is to issue analysis commands that are sent to each data server where they are then executed. These commands reshape data, run analyses, check outputs for disclosure and return these to the DataSHIELD client. DataSHIELD functions are designed to only output summary statistics that are typically low-dimensional, and are not directly disclosive, nor do they contain individual pateint data.
DataSHIELD is designed to be used alongside formal data governance policy as well as IT infrastructure best practice, and aligns with the Five Safes Framework – the international framework governing safe research access to data. Within the context of the Five Safes Framework the data custodian is responsible for policies and processes that mitigate the risk of data leak, information disclosure or data misuse, DataSHIELD can add an additional protective element to this.

You must be logged in to post a comment.